The security landscape of modern cloud-native systems is shifting fast, and one of the most dramatic changes is the explosive growth of non-human identities (NHIs). While human identities (employees, contractors, and users) have always been central to access control, today’s infrastructure also runs on countless machine identities, API keys, service accounts, workload credentials, IoT device IDs, and more.
According to Gartner, for every single human identity, organizations now manage between 45 and 80 NHIs. At enterprise scale, that means potentially hundreds of millions of machine identities in circulation. This rapid expansion of NHIs is creating a new attack surface that traditional identity and access management (IAM) models were never designed to handle.
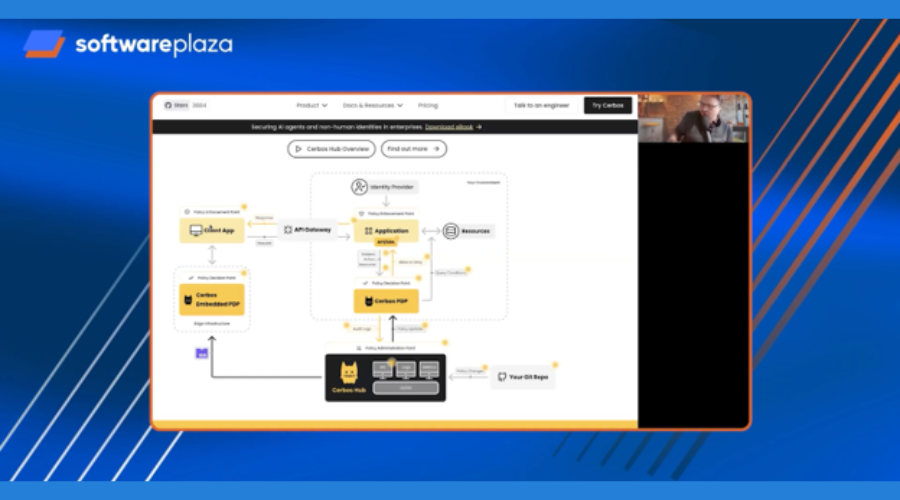
Cerbos, an open-source, policy-driven authorization platform, is addressing this challenge head-on, enabling real-time, zero-trust authorization for every workload and machine identity.
Why traditional identity management falls short for NHIs
Traditional IAM systems like Okta or Active Directory were designed with human users in mind. In these systems, a person authenticates using a username and password or through methods like SSO and MFA, after which the IAM platform assigns them roles and entitlements. Policies are then applied either at login or through periodic checks. This process works well for people, but becomes problematic when applied to non-human identities.
The lifecycle of NHIs is far more dynamic and often much shorter-lived. Service accounts, for example, may persist long after the workload they were created for is retired. CI/CD pipelines can generate credentials that remain valid indefinitely, and AI agents or ephemeral workloads may require credentials that last only seconds.
Without proper governance, these credentials can easily become long-lived, over-privileged, and effectively invisible to security teams. This runs counter to the principles of zero trust, such as enforcing least privilege and eliminating standing access.
The persistence of outdated practices, like manually creating service accounts, storing long-lived secrets in repositories or pipeline variables, and automatically trusting any request with valid credentials, has left many organizations with a vast pool of machine identities that are vulnerable to exploitation.
Cerbos’ Zero-Trust approach for NHIs
Cerbos was built as a stateless, identity-agnostic authorization engine. This architecture is uniquely suited to NHI security because it can make decisions in real time without maintaining complex state about every identity in the system.
Here’s how Cerbos applies zero-trust principles to NHIs:
1. Authorize every machine identity in real-time
Instead of granting blanket, long-lived privileges to an NHI, Cerbos authorizes each individual action against policy at the moment it is requested. This involves:
- Verifying both the human user (if applicable) and the workload identity handling the request
- Checking runtime context, such as namespace, cluster, trust domain, and even time of day
- Allowing or denying the action based on auditable, version-controlled policies
This approach ensures that no request is implicitly trusted, even if it comes from within the network or from a previously trusted workload.
2. Context-aware, multi-layer authorization
To truly implement zero trust for non-human identities, authorization must occur at multiple points across the system rather than being handled in a single layer. Cerbos can run at multiple layers in the stack:
- API Gateway Layer – coarse-grained checks on scopes, claims, and route access
- Service Mesh Layer – validating workload-to-workload calls using standards like SPIFFE/SPIRE
- Application Layer – fine-grained, contextual checks on user + workload + resource
By enforcing policies at every layer, Cerbos closes gaps where NHIs could otherwise bypass controls.
3. Stateless policy engine for ephemeral workloads
NHIs are increasingly short-lived, especially in AI agent workflows and serverless environments. Stateful authorization systems struggle here because they require syncing identity data before decisions can be made. Cerbos sidesteps this bottleneck:
- All context (user ID, workload ID, resource, action, etc.) is passed at request time
- Policies are evaluated entirely in memory, returning sub-millisecond decisions
- No replication or state sync delays, perfect for transaction-scoped identities
Managing the NHI lifecycle under Zero-Trust
Under a zero-trust model, managing the lifecycle of non-human identities requires careful attention to every stage of their existence. Creation should involve minting workload identities dynamically, with only the privileges necessary for the specific task at hand.
Rotation must be performed regularly, ensuring that when credentials are updated, the changes take immediate effect across the system. Revocation needs to be instantaneous when a workload completes, preventing orphaned credentials from lingering and becoming a target for attackers.
Attenuation plays a critical role as well; permissions should be tightly scoped to specific resources, environments, or time frames, limiting the potential damage if credentials are misused. This approach transforms NHIs from persistent, high-risk entities into short-lived, well-governed identities whose usage is always bound by contextual, real-time authorization checks.
Standards at the core
Cerbos is identity-source agnostic. It works with any identity provider (IdP) or workload identity system. This flexibility is enabled by its adoption of open standards:
- OAuth 2.0 / OIDC for authentication
- SPIFFE/SPIRE for workload identities
- ORZON (OpenID Foundation) for standardizing PDP (Policy Decision Point) interactions
- JWT & X.509 for secure, verifiable identity assertions
By aligning with open standards, organizations can integrate Cerbos into existing infrastructure without vendor lock-in and be confident that it will interoperate with future tools.
Why Cerbos stands out in the NHI security space
In a crowded identity and access control market, Cerbos’ differentiators for NHI defense are clear:
- Identity-agnostic: Works with any human or non-human identity source
- Truly stateless: No identity state replication, perfect for ephemeral workloads
- Granular contextual control: Combines user and workload context for precise enforcement
- Multi-layer enforcement: Runs at gateway, service mesh, and application levels
- Open source + open standards: Avoids lock-in and supports broad interoperability
This combination means organizations can apply zero-trust principles consistently, across every identity, every workload, and every layer of the system.
Final thoughts
The unprecedented rise of NHIs shows no sign of slowing. Without a shift to real-time, contextual, zero-trust authorization, the risks posed by unmanaged machine credentials will only grow. Cerbos offers a practical, standards-based approach that ensures every NHI is verified and authorized at the moment of use, with policies that are auditable, testable, and version-controlled. Its stateless architecture makes it a natural fit for environments where identities are ephemeral and workloads are highly dynamic.
By integrating Cerbos into their identity fabric, organizations can transform zero trust from a theoretical best practice into a functioning, operational reality, gaining both the agility and security needed to thrive in a machine-identity-dominated world.
This blog post is based on the webinar Zero Trust Authorization for Non-Human Identities: A Deep Dive with Alex Olivier, Co-founder & CPO at Cerbos. To watch the full video, click here.